Air Pollution Assessments
The purpose of this assessment is to determine the concentrations, sources, risk to human health and the impact of air quality on the environment from air pollutants.
Air quality assessment involves a number of components, including:
- collecting and validating air quality and meteorological data;
- compiling emissions inventories;
- modeling air quality and meteorological data; and
- analysing the data, inventories, and models in combination with other environmental and health data.
Environmental Impact Assessments
Environmental Impact Assessment is a formal process used to predict the environmental consequences (positive or negative) of a plan, policy, program, or project prior the implementation decision, it proposes measures to adjust impacts to acceptable levels or to investigate new technological solutions. Although it can lead to difficult economic decisions, strong political and social commitments, but it protects the environment which is a sound basis for effective and sustainable development.
Environmental Management Programmes
Environmental Management Plan: (EMP)
An Environmental Management Plan (EMP) can be defined as “an environmental management tool” used to ensure that undue or reasonably avoidable adverse impacts of the construction, operation and decommissioning of a project are prevented; and that the positive benefits of the projects are enhanced”. Environmental management is a deliberate, multi-disciplinary process, which requires careful preparation and planning. Information on natural and human activities, processes and systems must be gathered, plans and procedures decided upon, documents drawn up and systems implemented. EMPs are therefore important tools for ensuring that the management actions arising from Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) processes are clearly defined and implemented through all phases of the project life-cycle.
Environmental Noise
Environmental noise is the summary of noise pollution from outside, caused by transport. Industrial and Recreational activities. Noise is described as an unwanted sound and within this context environmental noise is generally present in some form in all areas of human activity. The effects of exposure to environmental noise may vary from emotional to physiological and psychological.
Ground Pollution
Soil contamination or soil pollution is caused by the presence of xenobiotic (human-made) chemicals or other alteration in the natural soil environment. It is typically caused by industrial activity, agricultural chemicals, or improper disposal of waste. The most common chemicals involved are petroleum hydrocarbons, polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (such as naphthalene and benzo(a)pyrene), solvents, pesticides, lead, and other heavy metals. Contamination is correlated with the degree of industrialization and intensity of chemical usage. The concern over soil contamination stems primarily from health risks, from direct contact with the contaminated soil, vapours from the contaminants, and from secondary contamination of water supplies within and underlying the soil.
Stack Sampling
Stack sampling implies the determination of emission characteristics and quantities at one particular time. This service is performed with portable equipment and under close supervision to ensure compliance with established procedures.
The essential elements of stack sampling include:
– Measuring of total gas (Volume)
– Measuring the amount of Sample withdrawn (Volume)
– Determining the amounts of specific Contaminant materials collected in the gas sample.
The objective of the stack sampling will be to give an accurate, precise and reliable determination of materials being released from a stack into the air.
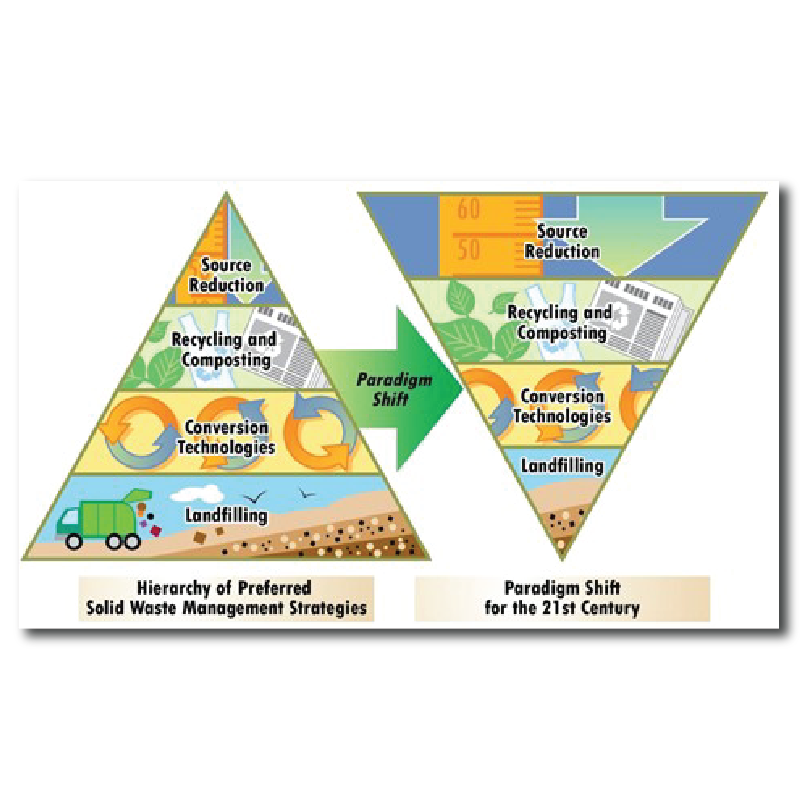
Waste Management
Waste management is the “generation, prevention, characterization, monitoring, treatment, handling, reuse and residual disposition of solid wastes”. There are various types of solid waste including municipal (residential, institutional, commercial), agricultural, and special (health care, household hazardous wastes, sewage sludge). The term usually relates to materials produced by human activity, and the process is generally undertaken to reduce their effect on health, the environment or aesthetics.
There is a wide array of issues relating to waste management and those areas include:
- Generation of waste
- Waste minimization
- Recycling and reuse
- Storage, collection, transport, and transfer
- Treatment
- Landfill disposal
- Environmental considerations
- Financial and marketing aspects
- Policy and regulations
- Education and training
- Planning and implementation.
Water Pollution Assessments
The overall process of evaluation of the physical, chemical and biological nature of water in relation to natural quality, human effects and intended uses, particularly uses which may affect human health and the health of the aquatic system itself.
Water quality assessment includes the use of monitoring to define the condition of the water, to provide the basis for detecting trends and to provide the information enabling the establishment of cause-effect relationships. Important aspects of an assessment are the interpretation and reporting of the results of monitoring and the making of recommendations for future actions.
In general, pollutants can be released into the environment as gases, dissolved substances, or particulate form. Ultimately pollutants reach the aquatic / water environment through a variety of pathways, including the atmosphere and the soil.